What will I experience?
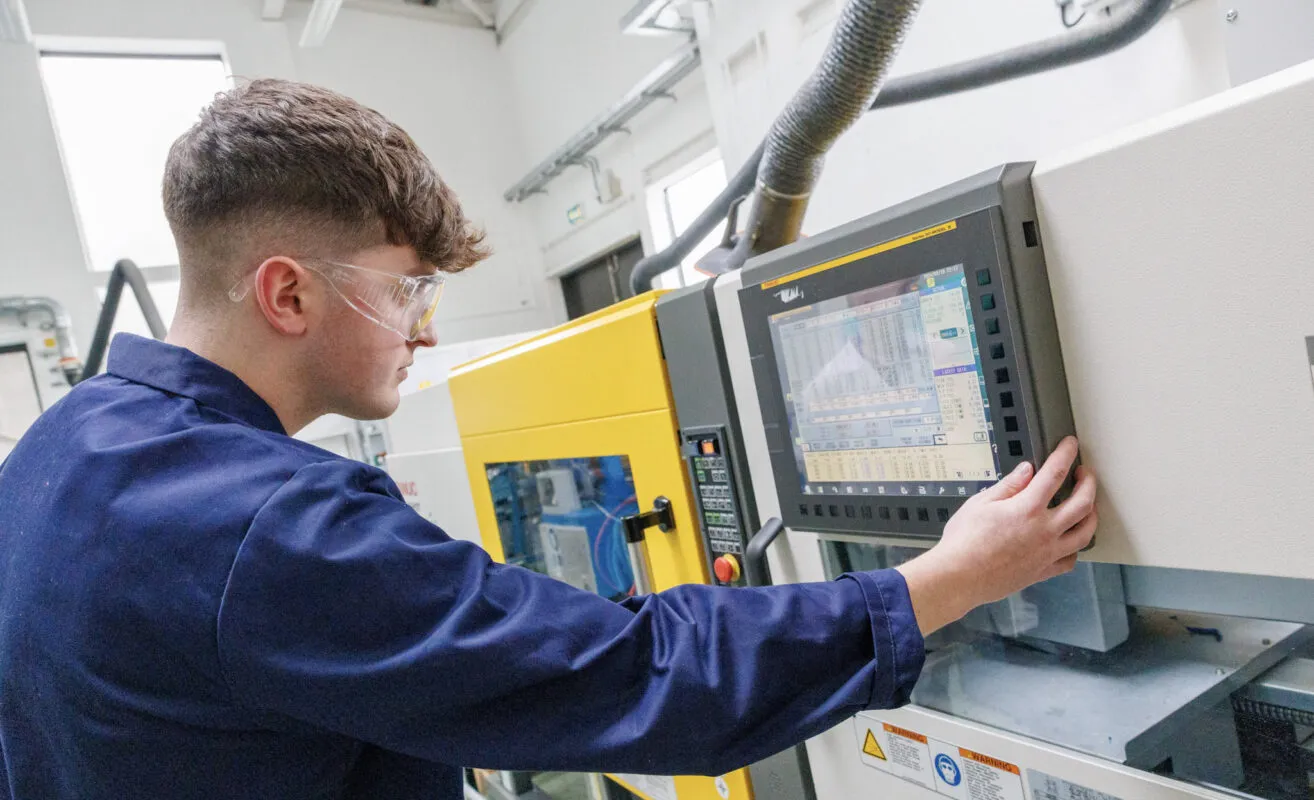
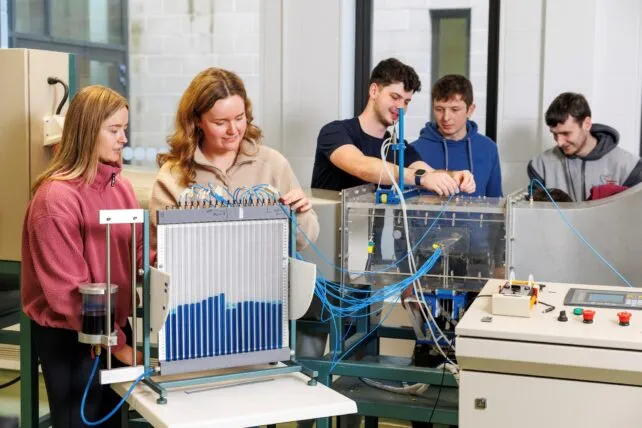
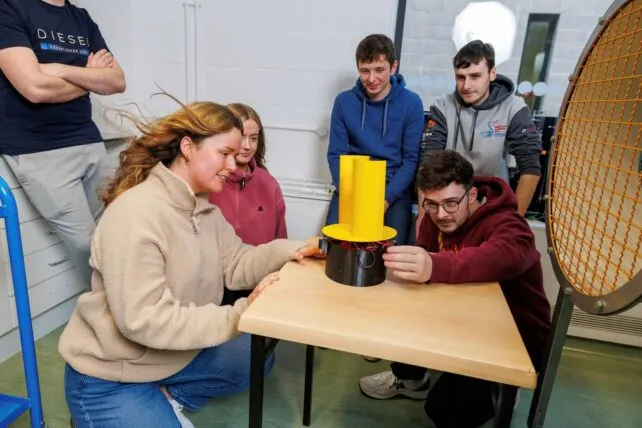
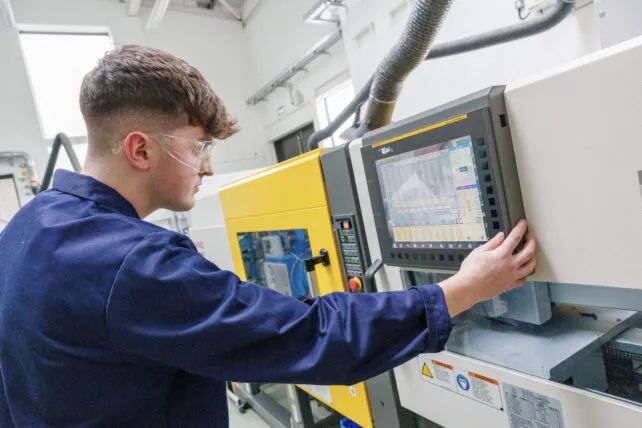
At TUS Midlands, Engineering education is heavily practical based. Approximately 50% of your time will be spent in state-of-the-art laboratories developing your practical engineering skills, and the other 50% will be spent on engineering theory and its application.
While studying on this course students will:
- Visit some of our industrial partners to experience the role of a polymer & mechanical engineer.
- Operate high-end polymer & mechanical technical engineering equipment in our cutting-edge engineering laboratories.
- Develop the ability to critically appraise polymer & mechanical engineering systems, to identify area of potential improvement, to bring about corrective action and where applicable, to suggest and implement an alternative solution.
- Learn about the environmental loadings of processes/plants and be committed to their reduction, either in terms of the product, the polymer materials or the process.
- Improve your teamwork and communication skills by working in part of small teams on problem-solving and projects.
- Develop an ethical awareness concerning the engineering profession and environment.
- Gain valuable work experience in 3rd year by completing a 6-month work placement.