Why study this course?
Our Mechanical Engineering with Energy course is crafted in a way to blend the essential theoretical and practical elements of Mechanical Engineering with some specialised expertise in sustainable energy engineering. Mechanical engineers are essential for optimizing energy usage in manufacturing processes and ensuring the efficiency of industrial machinery, while energy engineering assumes a pivotal role in the generation, distribution, and storage of energy, forming the cornerstone of our society. The dynamic landscape of technological progress, including electric vehicles and data centres, is continuously evolving, with mechanical engineers at the heart of the process.
Graduates can explore diverse career paths in renewable energy, manufacturing, and more, enjoying job security in an industry resilient to economic shifts. This field fosters innovation in energy technology, offers high earning potential, and aligns with personal interests in problem-solving and sustainable practices. Its global relevance allows professionals to work internationally and contribute to the transition to sustainable energy sources. Moreover, interdisciplinary learning opportunities broaden skill sets, making it a compelling choice for those seeking to shape a sustainable energy future.
What will I experience?
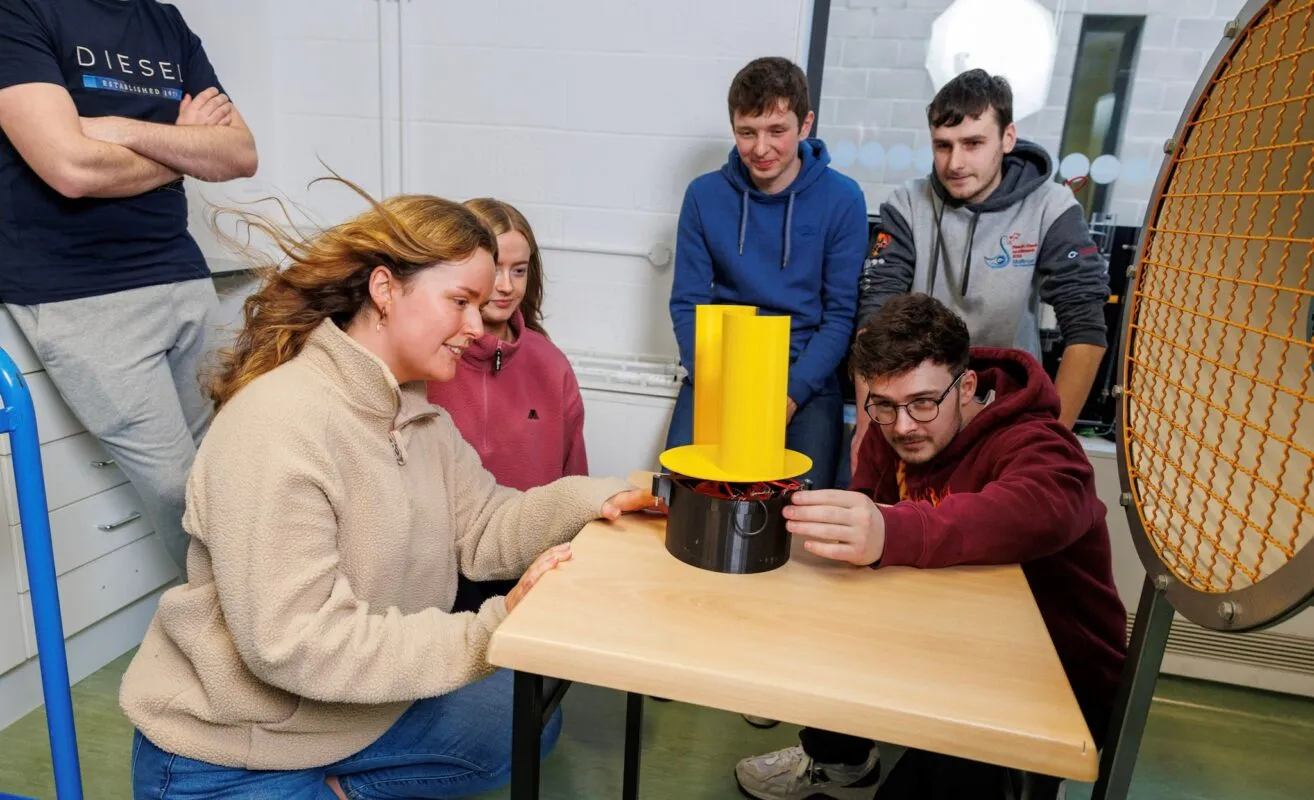
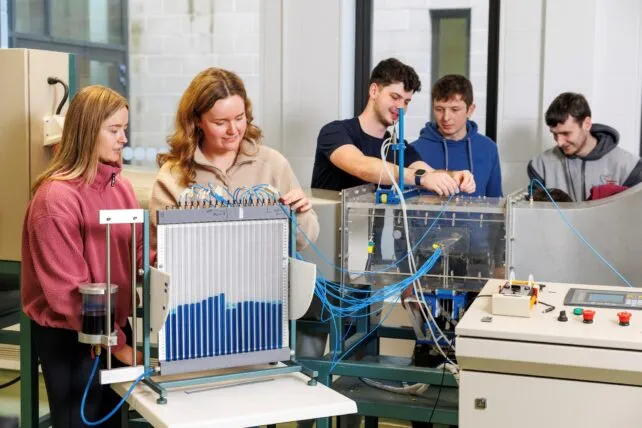
At TUS Midlands, Engineering education is very practical. Almost 50% of your time will be spent in state-of-the-art laboratories developing your practical engineering skills, and the other 50% will be spent on engineering theory and its application.
While studying on this course students will:
- Visit some of our industrial partners to experience the role of a mechanical engineer.
- Operate high-end technical engineering equipment in our cutting-edge engineering laboratories.
- Develop the ability to critically appraise mechanical engineering systems, to identify area of potential improvement, to bring about corrective action and where applicable, to suggest and implement an alternative solution.
- Learn about environmental loadings of processes/plants and be committed to its reduction, either in terms of the product, the materials or the process.
- Improve your teamwork and communications skills by working as part of small teams on problem-solving and projects.
- Develop an ethical awareness with regard to the engineering profession and environment.
- Gain valuable work experience in third year by completing a six month work placement, and in fourth year through an industry-focused project.
The student must complete a paid six-month placement from January to June in the programmes third year. Placements are readily available across all energy and manufacturing related industries and are intended for you to gain an insight into industrial best practices. These placements can be pursued both within Ireland and internationally. This placement carries a weight of 25 credits and must adhere to predetermined criteria, mutually agreed upon with the employer beforehand. The fourth year project will be organised in co-operation with industry and may in certain circumstances follow on from work initially carried out as part of your work placement.